Overview of the rising tide of food prices globally
In recent years, food prices have been on the rise globally, impacting vulnerable populations the most. The key factors driving this increase include climate change, political instability, and disruptions in supply chains due to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, the cost of essential food items such as grains, vegetables, and meats has skyrocketed, making it increasingly difficult for low-income individuals and families to afford nutritious meals.
The consequences of rising food prices are dire, leading to increased hunger and poverty around the world. Without access to affordable food, vulnerable populations are forced to compromise on the quantity and quality of their meals, which can have severe effects on their health and well-being. It is urgent to implement short-term solutions such as providing food aid and subsidies, as well as long-term solutions such as investing in agricultural development and climate resilience.
Governments, organizations, and researchers are taking specific actions to address the global food crisis, including creating sustainable farming practices, improving food distribution systems, and advocating for policies that support smallholder farmers. All stakeholders must work together to ensure that everyone has access to affordable and nutritious food, despite the challenges posed by rising food prices.
Factors contributing to the rise in food prices

In recent years, the cost of food has been on the rise, impacting households around the world. Several factors have contributed to this increase in food prices, making it difficult for many individuals and families to afford essential groceries. From climate change and environmental factors to global supply chain disruptions and changes in consumer demand, various elements at play have led to this trend. In this article, we will explore the key factors contributing to the rise in food prices and examine the potential impacts on both consumers and the food industry. Additionally, we will discuss the significance of understanding and addressing these contributing factors to mitigate the challenges posed by the increasing cost of food.
Nutritious foods and their importance in combating malnutrition

Access to safe and nutritious food is a fundamental human right, and it plays a vital role in addressing poverty, hunger, and inequality. Nutritious foods are essential for combatting malnutrition and improving overall health outcomes. For example, in low-income communities, access to nutritious foods can reduce the prevalence of malnutrition and its associated health problems, such as stunted growth and developmental delays. Additionally, nutritious foods can help break the cycle of poverty by providing individuals with the energy and nutrients they need to work and learn effectively.
Unfortunately, the impact of climate change and rising inequality has made it increasingly difficult for many people to access and afford nutritious foods. Climate change has led to disruptions in food production and distribution, resulting in unstable food supplies and higher prices, disproportionately affecting low-income communities. Moreover, rising inequality has widened the gap between those who can afford nutritious foods and those who cannot.
Local knowledge and solutions are crucial in promoting access to nutritious foods. By supporting local farmers and food producers, communities can ensure a sustainable and reliable supply of nutritious foods. Additionally, empowering individuals with the knowledge and resources to grow their nutritious foods can further combat malnutrition and improve overall health outcomes. Overall, access to nutritious foods is essential in combating malnutrition, addressing poverty and hunger, and promoting health and equality.
Impact of food prices on Latin American countries

The impact of rising food prices on Latin American countries has been significant, exacerbating existing challenges and leading to increased food insecurity, unemployment, and dependence on government assistance. The pandemic has further intensified these issues, with lockdowns and economic downturns contributing to a rise in hunger and poverty.
Countries such as Venezuela, Haiti, Argentina, and Mexico City are facing specific challenges in coping with the rising hunger crisis. Venezuela, for example, has been dealing with a severe economic and political crisis, leading to widespread food shortages and hyperinflation. Haiti has long struggled with poverty and food insecurity, further compounded by political instability. In Argentina, economic instability has led to food price increases, while Mexico City has seen a rise in unemployment and poverty due to the pandemic’s impact on the economy.
To address the food price impact and support vulnerable populations in the region, measures are being taken by governments and international organizations. These measures include the distribution of food aid, cash transfers, and food vouchers, as well as investment in agricultural and food production to improve self-sufficiency and reduce dependence on expensive imports.
Overall, the rising food prices have had a detrimental effect on Latin American countries, particularly in the context of the pandemic, but efforts are being made to mitigate the impact and support those most affected by the crisis.
Relationship between food prices and food shortage
The relationship between rising food prices and food shortage has become increasingly evident during the coronavirus pandemic. The pandemic has caused widespread disruptions in the food supply chain, leading to a surge in food insecurity among vulnerable populations. Supply shocks, such as border closures and lockdowns, have also contributed to global food inflation, making it even more challenging for people to access affordable and nutritious food. As a result, many individuals and families have experienced difficulties in obtaining enough food to meet their basic needs.
Furthermore, the potential effects of climate change on food production and distribution could exacerbate the situation. Extreme weather events and changing climatic patterns can lead to decreased crop yields and disruptions in food production, ultimately driving up food prices and exacerbating food shortages in various regions.
Overall, the interplay between the coronavirus pandemic, supply shocks, and the potential impact of climate change has highlighted the delicate balance between food prices and food shortage. These factors have brought food insecurity to the forefront of global concerns, underscoring the need for concerted efforts to address these challenges and ensure food security for all individuals.
The global food crisis and its consequences

The global food crisis has had far-reaching consequences on communities worldwide, with the issue stemming from a variety of factors such as climate change, geopolitical conflicts, and economic instability. The crisis has led to food shortages, rising prices, and increased food insecurity for many vulnerable populations. In addition to the impact on individuals and families, the food crisis also has broader implications for global health, economic stability, and political security. As the crisis continues to unfold, it is crucial to explore sustainable solutions that address the root causes while also prioritizing the immediate needs of those most affected. This includes finding ways to ensure access to nutritious and culturally appropriate food for all, while also addressing the environmental and ethical concerns inherent in the global food system. By taking a comprehensive and holistic approach, it may be possible to mitigate the consequences of the food crisis and work towards a more equitable and sustainable food future for all.
Challenges faced by low-income countries during times of crisis

Low-income countries face a myriad of challenges during times of crisis, from food insecurity to limited access to resources, economic downturns, and political instability. Food insecurity is a pressing issue as the availability and accessibility of nutritious food become even scarcer during crises. Limited resources further exacerbate this problem, hampering the ability of low-income countries to address food shortages and provide aid to their population.
Economic downturns also play a significant role in complicating matters, as they reduce the financial capacity of low-income countries to procure and distribute food, leading to increased vulnerability of their citizens. Political instability further hampers the ability of these nations to effectively respond to crises, as it creates an environment of uncertainty and hinders efficient decision-making.
Ultimately, these challenges have a profound impact on the ability of low-income countries to maintain stable economies and address food shortages. Without access to resources, financial stability, and political security, the task of addressing food insecurity becomes even more daunting for these nations.
Dependence on food imports and its implications
Morocco’s dependence on food imports has significant economic and geopolitical implications. As a country heavily relying on agricultural imports to meet its domestic food needs, Morocco faces the challenge of ensuring food security while managing the impact of fluctuating global food prices. This dependence also leaves the country vulnerable to geopolitical pressures, as any disruptions in food imports could have serious implications for the country’s economy and stability.
Furthermore, Morocco’s reliance on food imports affects global food security and the stability of food prices, particularly in regions heavily reliant on Morocco’s fertilizer exports. Any disruptions in Morocco’s fertilizer exports could have cascading effects on food production and prices globally, especially in regions that heavily rely on these fertilizers for agricultural productivity.
Managing the food-water-energy nexus is another key challenge for Morocco, with implications for the country’s economy and the global food supply. Addressing water scarcity, energy dependence, and food production is critical for ensuring food security and maintaining stable domestic and global food prices.
Overall, Morocco’s dependence on food imports has wide-ranging implications for its economy, global food security, and the stability of food prices in various regions.
Food price inflation and its effects on vulnerable populations
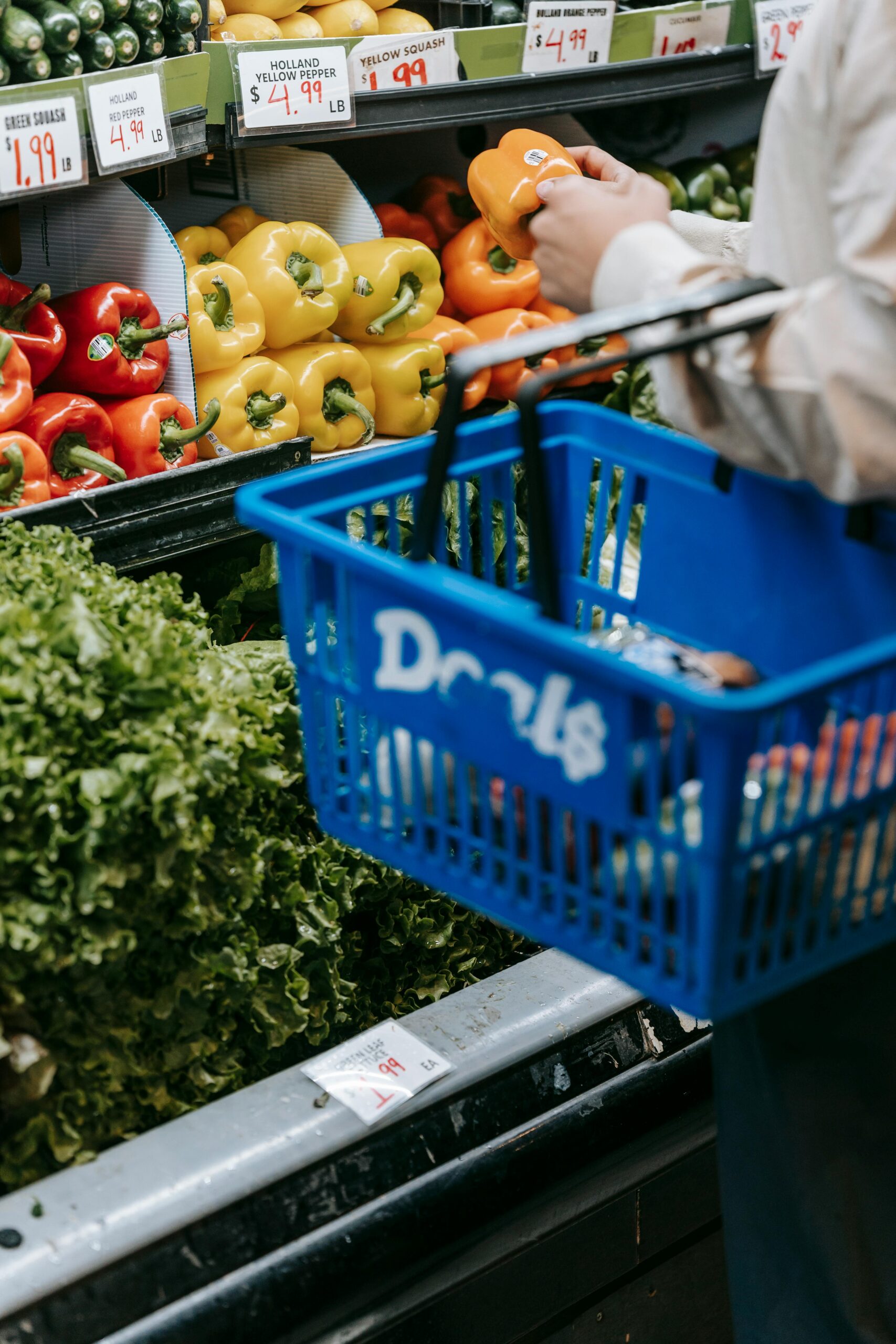

Food price inflation has had a severe impact on vulnerable populations around the world. The surge in global food insecurity has left many people struggling to afford the necessities, leading to malnutrition and hunger. This has also threatened progress in global health, as access to nutritious food is essential for overall well-being. Additionally, the implications for mass migration are significant, as people may be forced to leave their homes in search of better access to food.
Pandemic restrictions and economic downturns have further exacerbated the situation, making it difficult for people to access food and afford necessities. As a result, the crisis has deepened, particularly for those already living in poverty.
In response to these challenges, international institutions, governments, and aid organizations have taken action to mitigate the effects of food price inflation on vulnerable populations. This includes providing food aid, implementing social safety nets, and supporting small-scale farmers to improve food production. Additionally, efforts are being made to address the root causes of food price inflation, such as climate change and supply chain disruptions. These efforts must continue and expand to ensure that vulnerable populations receive the support they need during this challenging time.
Addressing the issue: Strategies for improving food security
Food security is a pressing issue that affects millions of people around the world. Ensuring access to safe and nutritious food is essential, and addressing the issue requires thoughtful and strategic solutions. In this article, we will explore various strategies for improving food security, taking into consideration the unique needs and challenges of different communities. By implementing these strategies, we can work towards creating a world where everyone has access to the food they need to thrive.
Agricultural production as a means to combat rising food prices
Agricultural production is vital in combatting rising food prices and reducing the threat of hunger and poverty. One strategy for increasing agricultural production is to invest in small-scale farmers by providing them with the necessary resources and training to improve their yields. Additionally, providing improved seeds and fertilizer can significantly boost agricultural production. Revitalizing support for research and innovation in agriculture is also key to developing new and more efficient farming techniques.
African heads of state must allocate 10 percent of their national budgets to agriculture. This investment has the potential to greatly reduce poverty by increasing food production, creating jobs in the agricultural sector, and stimulating economic growth in rural communities.
Global investment in agriculture is also essential to address rising food prices and food insecurity. By supporting agricultural development in developing countries, we can mitigate the impact of rising food prices and ensure that everyone has access to affordable and nutritious food.
In conclusion, a focus on agricultural production and investment in the agricultural sector is crucial to combatting rising food prices and reducing poverty. We must prioritize these efforts to ensure food security for all.
Focus on sub-Saharan Africa’s role in global agricultural production
Sub-Saharan Africa plays a crucial role in global agricultural production, with its vast expanse of arable land and favorable climate conditions. However, the region faces significant challenges in ensuring food security for its population and contributing to the global food supply. Undernourishment remains a pressing issue in many sub-Saharan African countries, and locust swarms have the potential to devastate crops and exacerbate food insecurity. Economic instability also poses a threat to agricultural development and food production in the region.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for African nations to enhance their contribution to the global food supply. Morocco’s fertilizer industry, for example, plays a vital role in supporting agricultural development in the region. By providing access to high-quality fertilizers, Morocco is helping to improve soil fertility and increase crop yields, ultimately boosting food production and security in sub-Saharan Africa.
The region’s potential in global agricultural production is significant, but addressing the impact of undernourishment, locust swarms, and economic instability on food security is crucial for maximizing this potential and ensuring a sustainable food supply for both the region and the world.
The role of international markets in stabilizing food prices
International markets have a significant impact on food prices, as seen through the effects of export bans, market volatility, and trade policies. Export bans, often imposed by countries in times of domestic shortage, can lead to price spikes in international markets as supply decreases. Market volatility, influenced by factors such as weather, geopolitical tensions, and global economic conditions, can also lead to fluctuations in food prices. Additionally, trade policies, such as tariffs and subsidies, can affect the cost of food in international markets.
However, international markets can also contribute to stabilizing food prices in times of crisis. When one region experiences a food shortage, international markets can provide essential food supplies, mitigating price spikes caused by domestic scarcity. In addition, trade agreements and policies can help ensure a steady flow of food products across borders, reducing the impact of export bans and market volatility on prices.
In conclusion, international markets play a crucial role in determining food prices, and their influence is felt through export bans, market volatility, and trade policies. While these factors can contribute to price instability, international markets also offer solutions for stabilizing food prices, especially in times of crisis.
The responsibility of the international community
When it comes to maintaining peace and stability in our world, the responsibility of the international community cannot be overstated. With conflicts and humanitarian crises occurring in various parts of the globe, the international community plays a crucial role in addressing these issues and promoting global cooperation. In this context, the ethical and moral responsibility of the international community becomes increasingly important in upholding values of justice, peace, and human rights.
Kosher aspects
In the realm of international relations and diplomacy, there is a kosher aspect to the responsibility of the international community. This entails conducting affairs in a manner that upholds ethical and moral standards, as well as respecting the diversity of cultures and beliefs around the world. The international community must navigate complex geopolitical issues while adhering to principles of fairness, transparency, and respect for human dignity. Additionally, the international community must ensure that its actions and decisions are in line with international law and norms, reflecting a kosher approach to global governance.
United Nations’ initiatives to address the global challenge of rising food prices

The United Nations has launched several initiatives to address the global challenge of rising food prices. These initiatives include investments in agriculture, improved bio-energy and trade policies, and programs targeting vulnerable people.
These initiatives aim to reduce the threat of hunger and poverty by increasing agricultural productivity and access to food. By investing in agriculture, the UN hopes to improve food security and reduce the vulnerability of communities to food price shocks. Additionally, the improved bio-energy and trade policies aim to promote sustainable food production and distribution, which can help stabilize food markets.
By targeting vulnerable people, these initiatives also aim to ensure that those most at risk of hunger and poverty have access to nutritious and affordable food. The ultimate goal of these initiatives is to reduce hunger, alleviate poverty, and create a more stable and sustainable food system.
In conclusion, the United Nations’ initiatives to address rising food prices aim to reduce hunger and poverty by investing in agriculture, improving bio-energy and trade policies, and targeting vulnerable populations.
How to save while shopping for food
1. Make a List of Items Needed: Before you go shopping, create a list of the food items you need. This will help you stay focused and avoid unnecessary purchases.
2. Compare Prices: Take some time to compare the prices of the same items at different stores. This can be done by visiting different grocery stores or checking their websites.
3. Look for Sales and Discounts: Keep an eye out for sales, discounts, or promotional offers on the items you need. These can be advertised in-store, in flyers, or online.
4. Use Coupons: Utilize coupons to save money on your grocery shopping. Look for coupons in magazines, newspapers, or online coupon websites.
5. Shop in Bulk: Consider buying non-perishable items or items with longer shelf lives in larger quantities. Buying in bulk can often lead to significant savings.
6. Check Unit Prices: Compare unit prices of different sizes or brands of the same item. Sometimes, buying a larger size may be more cost-effective in the long run.
7. Consider Store Brands: Try opting for store brands instead of popular brands. Store brands often offer similar quality at a lower cost.
8. Avoid Impulse Buying: Stick to your shopping list and avoid purchasing items on impulse. Impulse purchases can quickly add up and disrupt your budget.
Sources for this article
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/food-prices-skyrocketing-blame-4-120000614.html
https://www.csis.org/analysis/what-behind-recent-rise-global-food-prices
Recommend0 recommendationsPublished in Opinion
Responses